A single name has dominated headlines and dinner table conversations: ChatGPT.
Its ability to generate human-like text, answer complex questions, and even craft poetry has captivated the public imagination, leading many to wonder if their jobs are on the chopping block. Yet, while the fear of AI-driven job displacement is very real, the focus on ChatGPT might be a misdirection. The true seismic shift in the professional landscape isn’t being driven by conversational AI, but by a more sophisticated, autonomous, and often unseen force: AI Agents.
NOTE: This is an official Research Paper by “CLOXLABS“
To see the difference clearly, picture planning a complicated, multi-country trip. ChatGPT, in this case, is a fantastic, in-depth travel guide. It tells you everything you need about places to see, helps you line up an itinerary, and even translates menus and road signs. It’s a helpful companion, but you’re still the one picking the hotels, clicking “buy” on the flights, and wandering the new streets. You hold the map, using the guide to light the way.
Now think about an AI Agent. This time, the agent is your personal travel steward. Not just a friendly guide, but one who knows your favorites already, senses what you won’t like, and takes care of everything while you relax. The moment your flight is delayed, the agent rebooks the ticket before you feel the buzz of a notification. The clear skies you planned for suddenly turn to rain? The agent swaps your sightseeing for indoor charm and queues the next train. The agent doesn’t just hand you facts; it acts on them, making choices and carrying out plans without you lifting a finger. That’s the big difference, and it’s why AI Agents—not chatbots—are ready to reshape the way we work, play, and travel for good.
ChatGPT: The Familiar Face of AI (and Its Limitations)
ChatGPT, or any LLMs like it, have undeniably revolutionized how we interact with information. From drafting emails and summarizing lengthy documents to brainstorming creative ideas and even debugging code, its capabilities have made it an indispensable tool for millions. Its strength lies in its remarkable ability to understand and generate human-like text, making conversations feel natural and intuitive. It can process vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and produce coherent, contextually relevant responses at an astonishing speed. This conversational prowess has led to its widespread adoption in customer service, content creation, and even as a personal tutor.
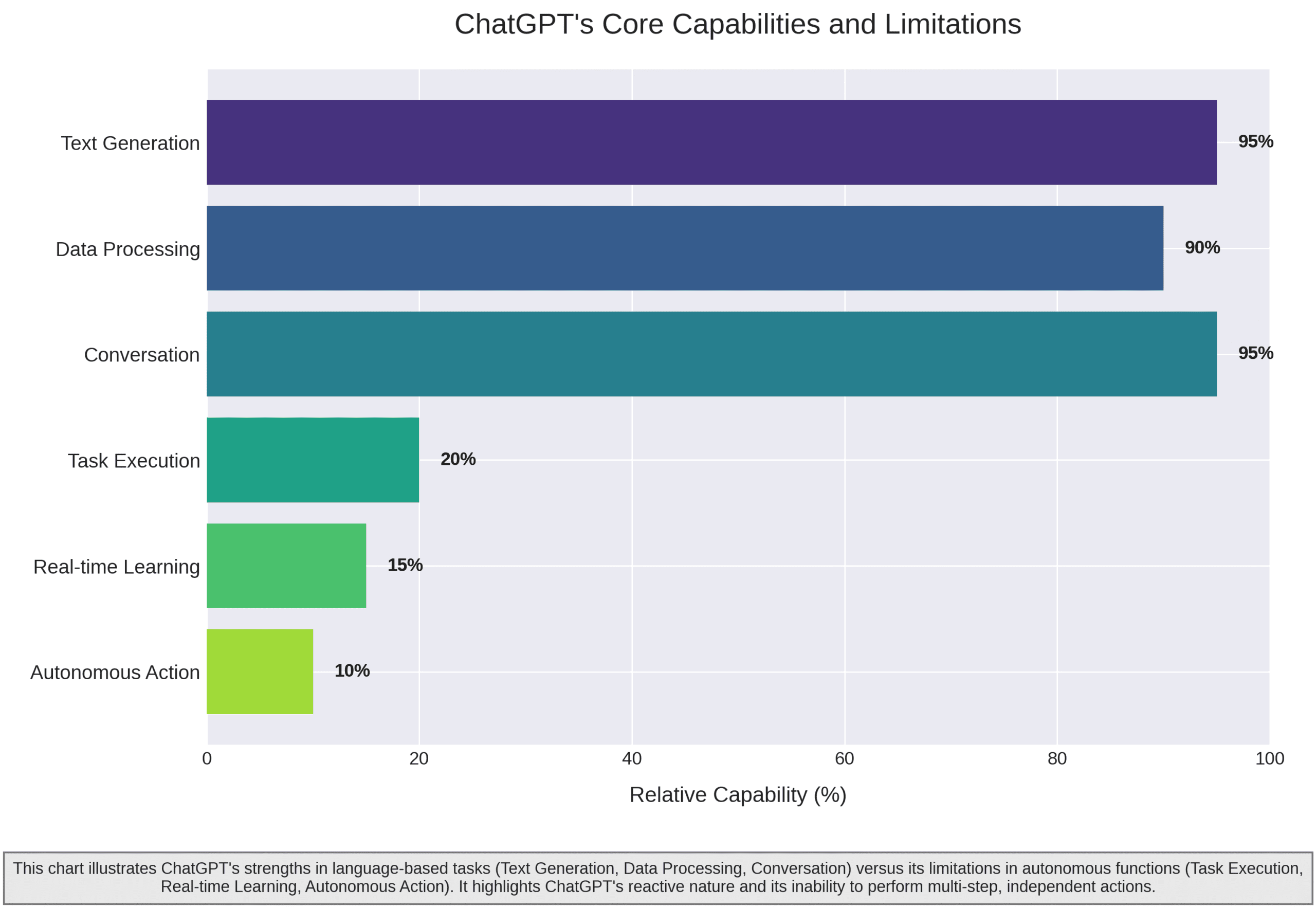
People are excited about ChatGPT, but it’s important not to forget what it can and cannot do. The model is amazing at processing language, but it’s still reactive. It waits for you to ask something, figures out an answer, and then types it back to you. It can’t start a task on its own, it can’t learn on the fly without a whole retraining cycle, and it can’t carry out a series of steps without being told each one. It has no will of its own. Picture it as the smartest consultant you’ve ever met: full of great ideas and data, but it won’t pick up the phone, it won’t send an email, and it won’t fly to a meeting to solve the issue. Its world is the text box you see; everything beyond that, including the real world and other software, stays out of reach.
Understanding this difference matters. ChatGPT can explain how to book a flight but can’t book the ticket itself. It can brainstorm a marketing plan but can’t send follow-up emails, schedule posts, or analyze what worked and what didn’t. Its strength lies in the information it generates, not in any actions it can carry out on its own. This is exactly why the next generation of AI is so important: it will take that output and turn it into real, automatic actions, changing everything we can do.
Enter the Autonomous Agent: A New Breed of AI
If ChatGPT is the eloquent conversationalist, then AI Agents are the silent, efficient doers. An AI Agent is an autonomous entity designed not just to process information, but to perform specific tasks or achieve particular goals independently. Unlike ChatGPT, which is primarily a language model, AI Agents are equipped with decision-making algorithms that allow them to analyze data, make choices, and take actions without constant human intervention. They are proactive, goal-oriented, and possess the ability to learn, adapt, and perform complex workflows across various digital environments.
The key difference lies in their operational paradigm. While ChatGPT waits for instructions, an AI Agent actively seeks to fulfill its objectives. It can utilize a suite of tools, interact with different software applications, and even learn from its experiences to improve its performance over time. This autonomy enables them to tackle multi-step processes that would be impossible for a traditional LLM alone. For instance, an AI Agent might search the web for information, synthesize findings, generate a report, and then email it to relevant stakeholders—all without a human guiding each individual step.
Consider the practical implications across various sectors:
• Healthcare: AI Agents can monitor patient vitals in real-time, predict disease outbreaks based on epidemiological data, and even assist in diagnostic processes by cross-referencing symptoms with vast medical databases.
• Finance: They can detect fraudulent transactions by identifying unusual patterns, optimize investment portfolios by analyzing market trends, and automate compliance checks, significantly reducing manual oversight.
• Manufacturing: AI Agents can control robotic systems on an assembly line, predict equipment failures before they occur, and optimize supply chains by dynamically adjusting to disruptions.
• Personal Assistance: Beyond simple scheduling, an advanced AI Agent could manage your entire digital life, from organizing your inbox and filtering spam to researching complex topics and even handling customer service interactions on your behalf.
This is where agents like Manus come into play. Manus is designed as an autonomous general AI agent, capable of operating in a sandboxed virtual machine environment with internet access. It can leverage shell commands, interact with web browsers, use text editors, and even install additional software to achieve open-ended objectives. Manus exemplifies the capabilities of these new AI agents: not just understanding language, but understanding intent, planning complex actions, and executing them across diverse digital tools to achieve a user’s goal. It’s a significant leap from merely generating text to actively performing work.
The Shifting Landscape of Work: Beyond Job Displacement
The conversation around AI and jobs often devolves into a binary fear: will AI take my job, or won’t it? The reality, as always, is far more nuanced. While statistics can be alarming—with some reports suggesting AI could displace tens of millions of jobs globally by 2030 the narrative needs to shift from simple replacement to profound transformation. The true threat isn’t AI itself, but rather the failure to adapt to a world where AI is an integral part of the workforce. As Roberto H. Luna, CEO of Lunivate, aptly puts it: “It’s not about AI taking your job, it’s about someone using AI taking your job. And if you’re not paying attention, that’s exactly what’s going to happen”.
AI Agents are not merely automating repetitive, manual tasks; they are increasingly capable of handling complex, multi-step processes that once required significant human cognitive effort. This means that roles traditionally considered safe from automation, particularly in white-collar sectors, are now within the purview of AI. For instance, AI could replace over 50% of tasks performed by market research analysts and sales representatives [8]. Entry-level white-collar jobs are particularly vulnerable, with some predictions suggesting up to half could be impacted.
However, this isn’t necessarily a doomsday scenario. Instead, it’s an urgent call for re-evaluation and adaptation. The automation driven by AI Agents frees up human capital from what many describe as “soul-crushing tasks”. Imagine the hours spent on data entry, report generation, or routine customer inquiries. When AI Agents handle these, human employees are liberated to focus on higher-value activities that demand creativity, critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and complex problem-solving—skills that remain uniquely human. This is the essence of augmentation, not just replacement. AI Agents become powerful co-pilots, extending human capabilities and allowing us to achieve more with less effort.
This shift demands a proactive approach from both individuals and organizations. The jobs of the future will increasingly involve collaborating with AI, overseeing AI Agents, and leveraging their capabilities to innovate. Those who embrace this partnership, understanding how to effectively train, manage, and integrate AI into their workflows, will be the ones who thrive in the evolving economy. The focus moves from what tasks are performed to how tasks are performed, with AI taking on the heavy lifting of execution, and humans providing the strategic direction, oversight, and creative spark.
Navigating the Future: Adapting to the Agent Economy
The rise of AI Agents presents both challenges and unprecedented opportunities. For individuals, the imperative is clear: continuous learning and adaptation are no longer optional but essential for career longevity. This means:
• Upskilling in AI-Related Tools: Familiarize yourself with how AI Agents work, how to interact with them, and how to leverage their capabilities. Understanding prompt engineering, data interpretation, and AI workflow management will become increasingly valuable skills.
• Focusing on Uniquely Human Skills: While AI excels at logic and execution, human strengths in creativity, critical thinking, emotional intelligence, complex problem-solving, and interpersonal communication remain irreplaceable. Cultivating these “soft skills” will differentiate human workers in an AI-augmented world.
• Embracing a Growth Mindset: The pace of technological change will only accelerate. A willingness to learn new things, unlearn old habits, and adapt to evolving roles will be crucial for navigating the agent economy successfully.

For businesses, the strategic integration of AI Agents is no longer a competitive advantage but an existential necessity. Companies that fail to develop a robust AI strategy risk being outpaced by more agile competitors. Key strategies include:
• Investing in AI Agent Integration: Identify areas where AI Agents can automate routine or complex tasks, streamline workflows, and enhance productivity. This requires careful planning and often a significant investment in new technologies and infrastructure.
• Training and Reskilling Employees: Instead of viewing AI as a threat to the workforce, businesses should invest in training programs that equip employees with the skills to work alongside AI Agents. This fosters a culture of collaboration and innovation, turning potential displacement into augmentation.
• Fostering a Culture of Innovation: Encourage experimentation with AI Agents and create an environment where employees feel empowered to explore new ways of working. This includes establishing clear ethical guidelines for AI deployment and ensuring data privacy and security.
The future of work is not about humans versus machines, but about humans with machines. The most successful individuals and organizations will be those that master the art of human-agent collaboration, leveraging the strengths of AI to amplify human potential.
Conclusion: The Human-Agent Partnership
The narrative surrounding artificial intelligence is rapidly evolving. While ChatGPT opened our eyes to the incredible power of generative AI, it is the rise of autonomous AI Agents that truly signals a paradigm shift in how we work, create, and interact with the digital world. These agents, capable of independent decision-making, proactive task execution, and continuous learning, are moving beyond mere information processing to become active participants in our professional and personal lives.
The fear of job displacement is a valid concern, and indeed, many roles will be transformed. However, the more accurate and empowering perspective is that AI Agents are not here to replace humanity, but to augment it. They are poised to take on the mundane, the complex, and the time-consuming, freeing us to engage in work that is more strategic, creative, and uniquely human. The future belongs to those who embrace this human-agent partnership, understanding that the most powerful intelligence emerges when human ingenuity collaborates with autonomous AI.
As we stand on the cusp of this new era, the call to action is clear: educate yourself, adapt your skills, and engage with the evolving AI landscape. The future of work isn’t about AI taking your job; it’s about AI transforming your job, and empowering you to achieve more than ever before. The question is not if AI will change your world, but how you will choose to shape your place within it.
References
[1] Forbes: Why AI Agents—Not ChatGPT—Will Dominate 2025 – https://www.forbes.com/sites/torconstantino/2025/01/29/why-ai-agents-not-chatgpt-will-dominate-2025/
[2] Heliverse: AI Agents vs. ChatGPT: Understanding the Real Differences in 2025 – https://www.heliverse.com/blog/ai-agents-vs-chatgpt-understanding-the-real-differences-in-2025
[3] Heliverse: AI Agents vs. ChatGPT: Understanding the Real Differences in 2025 – https://www.heliverse.com/blog/ai-agents-vs-chatgpt-understanding-the-real-differences-in-2025
[4] Forbes: Why AI Agents—Not ChatGPT—Will Dominate 2025 – https://www.forbes.com/sites/torconstantino/2025/01/29/why-ai-agents-not-chatgpt-will-dominate-2025/
[5] Heliverse: AI Agents vs. ChatGPT: Understanding the Real Differences in 2025 – https://www.heliverse.com/blog/ai-agents-vs-chatgpt-understanding-the-real-differences-in-2025
[6] Exploding Topics: 60+ Stats On AI Replacing Jobs (2025) – https://explodingtopics.com/blog/ai-replacing-jobs
[7] Goldman Sachs Report (cited in Forbes): 300 million jobs could be lost to AI, affecting 25% of the global labor market.
[8] World Economic Forum (cited in Bloomberg): AI could replace over 50% of tasks for market research analysts (53%) and sales representatives (67%).
[9] Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei (cited in Jacobin and Axios): AI could wipe out half of all entry-level white-collar jobs and spike unemployment to 10-20% in the next 1-5 years.








